Want to create middleware in ExpressJs without the guesswork? This Express.js middleware tutorial will show you, through an example, how to create custom Express.js middleware that you can later reuse in any real project. You are going to learn how to write an Express.js middleware function, plug it into routes, and test it fast.
By the end, you will log requests, secure endpoints with a simple API key, and handle errors cleanly. These patterns fit everyday apps like dashboards, e‑commerce, and microservices.
What is middleware in ExpressJs and Nodejs?
ExpressJs middleware is a function that sits between a request hitting your server and your route’s final response. It gets passed req, res, and a next function. You can execute code, modify the request, end the response, or call next to pass control to the next middleware. Below are common use cases:
- Logging and metrics
- Authentication and API key checks
- Input validation and sanitization
- Setting headers and CORS
- Error handling
Project Setup and Installation
Let’s create new Node.js application and install Express in it. You can use any other application you have. For this post, we will create new application using below command:
mkdir express-mw-demo
cd express-mw-demo
npm init -y
npm install express
touch index.jsThe above commands, will create new Node.js application and install express JS in it. We have also added index.js file which will be used as server file.
How to Create Middleware in ExpressJs With Example
Let’s take an example to create custom middleware. This middleware logs incoming requests to the console for now. You can customize this for logging data into database.
const requestLogger = (req, res, next) => {
const start = Date.now()
res.on('finish', () => {
const ms = Date.now() - start
console.log(req.method + ' ' + req.originalUrl + ' ' + res.statusCode + ' ' + ms + 'ms')
})
next()
}As per above middleware code, it will process each incoming request and logs request’s method, URL and status code. It will not impact anything on request output. Let’s take full example with different middleware and implementation.
const express = require('express')
const app = express()
const PORT = 3000
app.use(express.json())
const requestLogger = (req, res, next) => {
const start = Date.now()
res.on('finish', () => {
const ms = Date.now() - start
console.log(req.method + ' ' + req.originalUrl + ' ' + res.statusCode + ' ' + ms + 'ms')
})
next()
}
const attachRequestId = (req, res, next) => {
const id = Math.random().toString(36).slice(2, 10)
req.id = id
res.setHeader('X-Request-Id', id)
next()
}
const requireApiKey = (req, res, next) => {
const key = req.header('x-api-key')
if (key !== 'secret123') {
return res.status(401).json({ error: 'Unauthorized' })
}
next()
}
app.use(attachRequestId)
app.use(requestLogger)
app.get('/health', (req, res) => {
res.json({ ok: true, id: req.id })
})
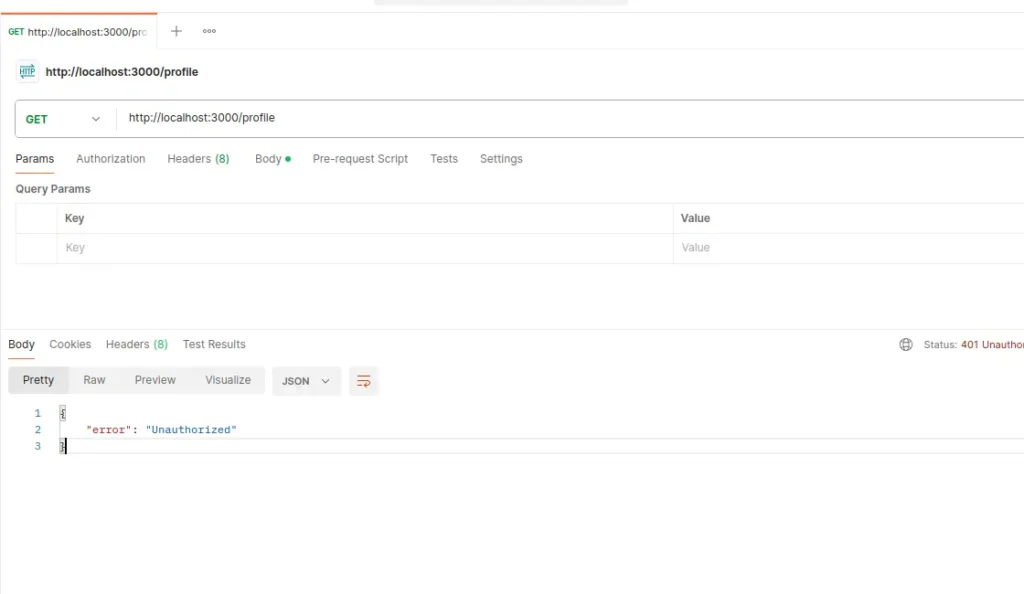
app.get('/profile', requireApiKey, (req, res) => {
res.json({ user: 'Ava', plan: 'Pro', id: req.id })
})
app.post('/echo', (req, res) => {
res.json({ received: req.body, id: req.id })
})
const errorHandler = (err, req, res, next) => {
res.status(500).json({ error: 'Internal error', id: req.id })
}
app.use(errorHandler)
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log('http://localhost:' + PORT)
})In above script, We have defined two additional middlewares. One is for attaching unique request ID as header and another one is for checking require API Key. The request logger and request ID middleware is applied on all routes. However the middleware for API is applied only on profile API.
Here, when user try to access profile API it will check for API key. For now, we have kept API key as static but you can customize it for checking from database.
Run and test application
To run and test Node.js application, you need to start server. Open your terminal and enter below command:
node index.jsIt will start server. Now we will use postman to test this endpoints.
Conclusion
You now have a clear example and implementation of Express.js custom middleware that you can adapt quickly. Start small, compose focused middleware, and maintain your order. As you scale, this approach helps you test behavior and ship faster.
Learn how to handle user-submitted data efficiently in your Express applications by exploring our detailed guide on Retrieve and Process Form Data via POST in Express JS. It walks you through capturing and managing form data using POST requests with clear examples.

